In today's globalized food industry, ensuring the safety and quality of food products is of utmost importance. Food safety professionals and food processing executives understand that adhering to rigorous standards is essential. One such standard that plays a pivotal role in food safety management is the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI). In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of conducting successful Food Safety Management Reviews (FSMR) under the GFSI scheme. We will explore the significance of GFSI, provide a step-by-step approach to conducting FSMRs, and highlight how modern technology, including food safety software and food traceability software, can streamline the process.
The Significance of GFSI
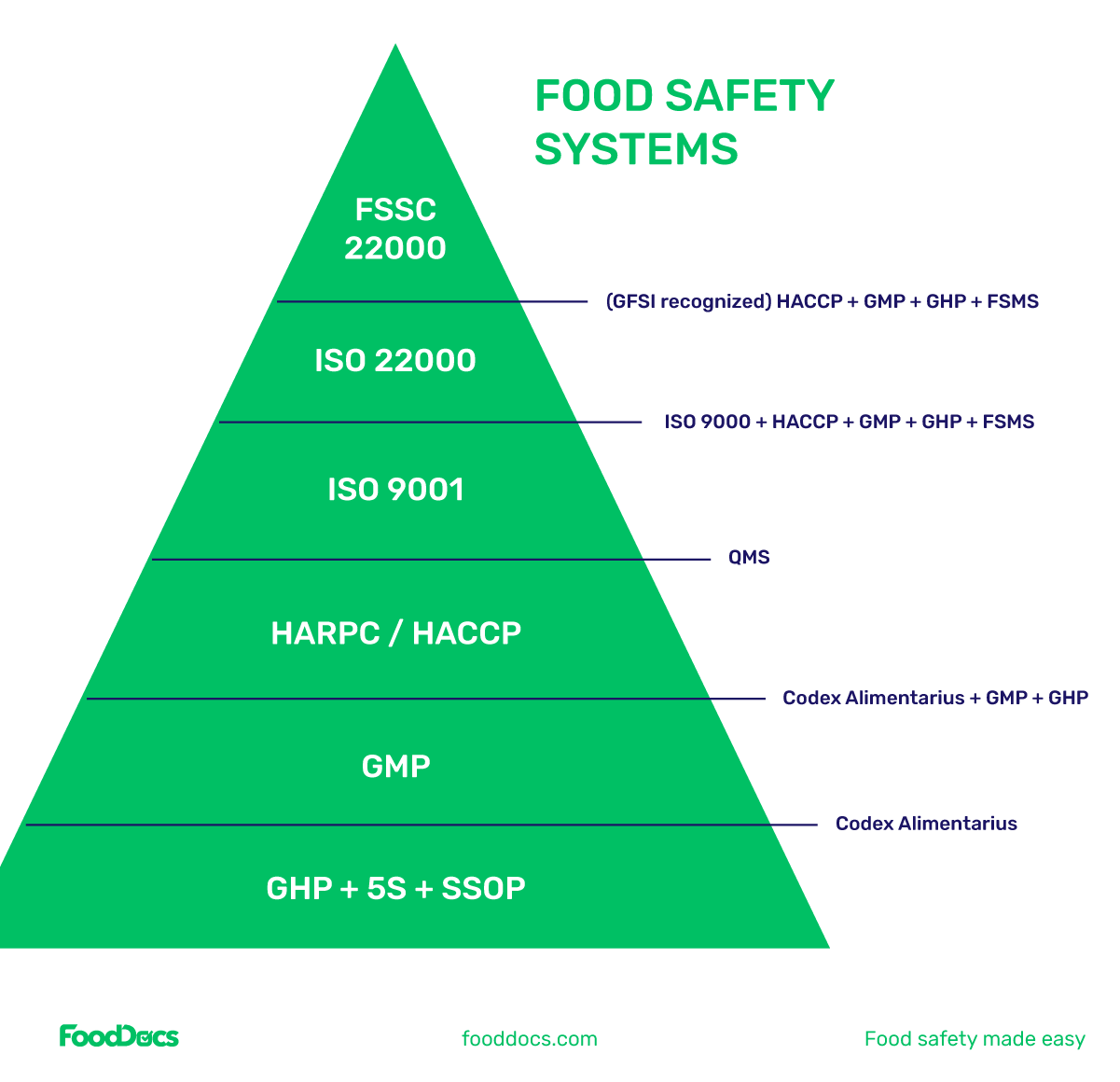
The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is a global collaboration of leading food safety experts, retailers, and manufacturers committed to ensuring the safety and quality of food products throughout the supply chain. GFSI benchmarks and recognizes various food safety management schemes, such as BRCGS, SQF, and FSSC 22000, to provide a unified approach to food safety standards.
Why is GFSI Important?
-
Harmonization: GFSI harmonizes food safety standards, reducing duplication of efforts and providing consistency in safety requirements across the industry.
-
Global Trade: GFSI certification is widely recognized, facilitating international trade by ensuring that food products meet high safety and quality standards.
-
Consumer Trust: GFSI-certified products inspire consumer confidence, as they are associated with robust safety practices and quality control.
-
Risk Mitigation: Compliance with GFSI standards helps mitigate the risk of foodborne illnesses, recalls, and reputational damage.
Conducting Successful Food Safety Management Reviews (FSMR)
Now, let's explore a step-by-step approach to conducting successful FSMRs under the GFSI scheme. This process is crucial for food safety professionals and food processing executives to ensure compliance and continuous improvement.
Step 1: Understand GFSI Standards
Begin by thoroughly understanding the specific GFSI standard relevant to your organization. Each standard has its requirements, so it's essential to be well-versed in the standard you are pursuing.
- Example: If your organization is following the BRCGS standard, familiarize yourself with its latest version and requirements.
Step 2: Assemble Your Team
Gather a cross-functional team that includes members from various departments, such as quality assurance, production, and supply chain. Collaboration is key to a successful FSMR.
- Example: Your team may include a quality manager, a production supervisor, a compliance officer, and a food safety specialist.
Step 3: Review Documentation
Collect and review all relevant documentation, including your organization's food safety manual, policies, procedures, and records. Ensure that all documentation is up-to-date and aligned with the chosen GFSI standard.
- Example: Review your organization's HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) plan, which is a fundamental requirement in many GFSI standards.
Step 4: Gap Analysis
Conduct a thorough gap analysis to identify areas where your current food safety management system falls short of the GFSI standard's requirements. This analysis helps you pinpoint areas that require improvement.
- Example: If the GFSI standard requires enhanced traceability, assess your current traceability processes and identify gaps.
Step 5: Corrective Actions
Based on the gap analysis findings, develop a corrective action plan. Assign responsibilities and deadlines for addressing the identified gaps and non-conformities.
- Example: If your gap analysis revealed that you lack a robust supplier approval process, your corrective action plan might involve implementing a supplier evaluation system.
Step 6: Implementation
Execute the corrective action plan, making the necessary changes to your food safety management system. Ensure that all employees are trained on the updated procedures and processes.
- Example: Train production staff on new sanitation procedures that align with GFSI standards.
Step 7: Internal Audits
Conduct internal audits to verify the effectiveness of the corrective actions and ensure compliance with the GFSI standard. Internal audits should be performed regularly to identify and address issues promptly.
- Example: An internal audit may reveal that some employees need additional training on allergen control procedures.
Step 8: Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a core principle of GFSI. Establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring, measurement, and enhancement of your food safety management system.
- Example: Implement a system for tracking and analyzing customer complaints to identify recurring issues and opportunities for improvement.
Leveraging Technology for FSMR Success
In today's fast-paced and data-driven world, technology plays a crucial role in streamlining FSMRs and ensuring compliance with GFSI standards. Let's explore how food safety software and food traceability software can enhance the FSMR process.
Food Safety Software: A Game-Changer
Food safety software is designed to automate and streamline various aspects of food safety management. Here's how it can benefit FSMRs:
-
Data Centralization: Food safety software centralizes critical data, making it easily accessible during an FSMR. This includes documentation, audit reports, and corrective action plans.
-
Real-time Monitoring: These tools enable real-time monitoring of critical control points and key performance indicators, ensuring that your food safety management system is always on track.
-
Audit Management: Food safety software simplifies audit preparation and management by organizing and storing relevant documents and records.
-
Traceability: Traceability features in food safety software help track ingredients and products throughout the supply chain, aligning with GFSI requirements.
Food Traceability Software: Enhancing Transparency
Food traceability software focuses on tracking the movement of food products and ingredients from their source to the consumer. Here's how it complements FSMRs:
-
Supplier Verification: Traceability software enables quick verification of supplier information and product origins, a crucial aspect of GFSI compliance.
-
Recall Management: In the event of a recall, food traceability software helps identify affected products swiftly and accurately, minimizing potential risks.
-
Data Analytics: Traceability software provides valuable data analytics that can be used to improve supply chain efficiency and food safety measures.
Example: XYZ Foods Implements Food Safety Software
To illustrate the impact of food safety software on FSMRs, let's look at a hypothetical case study involving XYZ Foods, a leading food processor.
XYZ Foods faced challenges in managing their extensive food safety documentation and ensuring compliance with the BRCGS standard. They decided to implement food safety software from a provider like NORMEX.
-
Efficiency Improvement: With NORMEX's food safety software, XYZ Foods achieved significant efficiency improvements. They were able to digitize and centralize their documentation, reducing the time and effort required for document retrieval during FSMRs.
-
Real-time Monitoring: The software provided real-time monitoring of critical control points, allowing XYZ Foods to identify and address deviations promptly.
-
Audit Management: NORMEX's software streamlined audit management, simplifying the preparation and execution of FSMRs.
-
Traceability: XYZ Foods enhanced their traceability practices with the software, ensuring they could quickly trace the origin of any ingredient or product, aligning with GFSI requirements.
In conclusion, successful FSMRs are not just about meeting compliance requirements but also about safeguarding consumer health and trust. The commitment to food safety management and the integration of technology are key drivers in achieving GFSI certification and ensuring the highest standards of food safety in today's global food industry.